Definition of Simulation Shape Properties
When a shape is selected on a diagram and a user selects “Properties” the Simulation Properties window opens and a user may configure simulation parameters related to that shape.
Note: If you use BPMN Shapes in your simulation diagram, please be aware that correct behavior for each Flow Object must be given, as it is for all shapes of any diagram type. You may want to see our BPMN Shape Behavior Guide for more information, particularly after reviewing the pages below.
Generator
Any shape can be configured to have cases generate at that shape.
To do this, toggle on the “Generate Here” option.
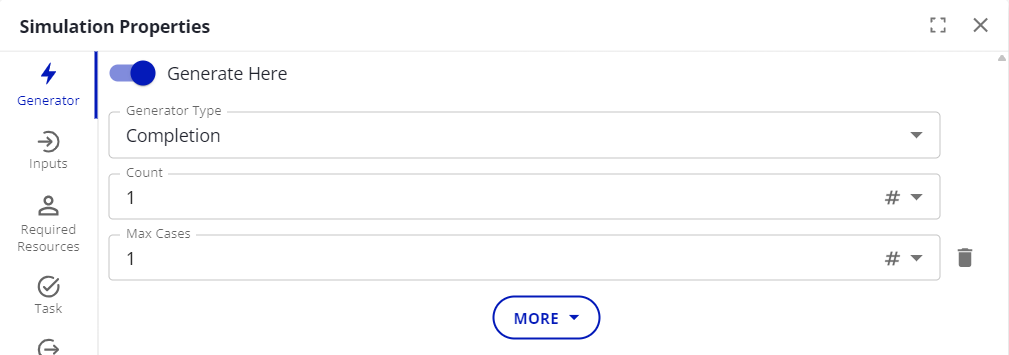
Generator Type
Completion: The generator will generate more cases when the first group generated finishes.
Interval: The generator will generate cases once per interval.
Timer: The generator will generate cases each time the timer triggers. See the Timers tab on the Simulation Properties page.
External Data: Import an Excel file containing data for when cases generate. See External Data Generator for how to use this.
Message: The generator will generate cases when it receives a specified message from the specified messaging partner. Cases generated in this way will be correlated with the triggering case.
Variable Change: The generator will generate case(s) when a variable (e.g., a Model variable) meets one of the following conditions:
Increased - The value of the variable increases (e.g., goes from false to true, from 0 to 1, etc.)
Decreased - The value of the variable decreases (e.g., goes from true to false, from 1 to 0, etc.)
Changed - The value of the variable changes (e.g., goes from 31 to 42, from false to true, from true to false, etc.)
Assigned - The value of the variable is assigned. Even if it still has the same value (e.g., the value was 42 and is assigned again, and yet remains at 42) an assignment to the variable will trigger the generator.
There are other properties that may be available, depending on the generator type:
Count
The number of cases that generate each time.
Interval
The time to wait in between generations, for an Interval generator.
Max Cases
The generator will stop after generating this many cases.
Inputs
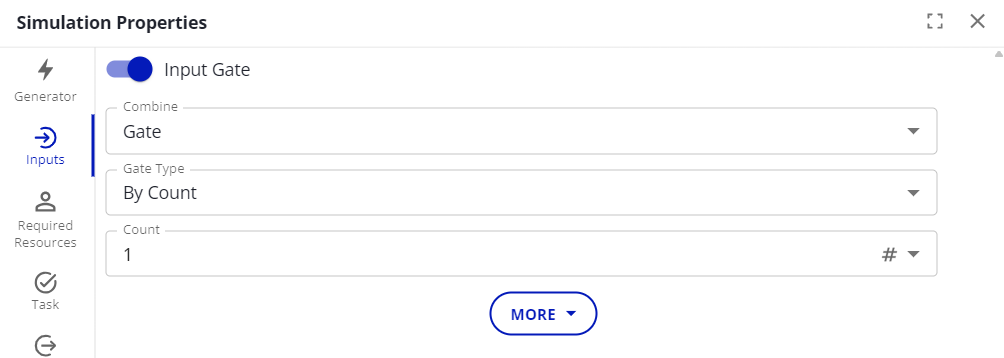
This is used for blocking cases before they enter the activity. To do this, toggle on the “Input Gate” option.
Combine
Specifies what happens to cases that pass through the gate together.
Gate: Nothing additional happens. The cases pass through the gate.
Batch: The cases are batched into a single case. They can be unbatched later with an Unbatch gate.
Join: Create a new case by combining the cases. If combining an entire case family, this will be the original case.
For cases that are part of a family, only cases that are in the same family will be joined. For example, if the gate type is From Input Paths, then it will wait for one case from each input path from the same family. If the gate type is Count, it will wait until there are that number of cases from the same family, and join them.
For cases that have no family, they will be joined together. For example, if Count is 5 it will wait for 5 with no family, and join those.
Gate Type
By Count: Cases will wait until a certain number are present, then they will all pass at the same time.
By Family: Cases will wait until the entire case family is present, then they will all pass at the same time.
By Time: Cases will wait and be released every time the specified interval passes.
By Expression: Cases will wait until the specified expression evaluates to true.
By Timer: Cases will pass each time the timer triggers.
By Enumerated Type: Cases will wait until for each unique value of the enumerated type, there is a case with that value of the enumerated type for the specified variable. Then those cases will all pass at once.
From Input Paths: Cases will wait until there is one case for each connector line leading into the activity. Then those cases will all pass at once.
Delay: Each case will wait for a specified time, and then pass.
Unbatch: Batched cases will unbatch upon reaching this gate, and then pass.
Multiple: Make a combination of Time and Expression gates.
Until message: Cases will wait for a specified message from a correlated case from the specified process.
Required Resources
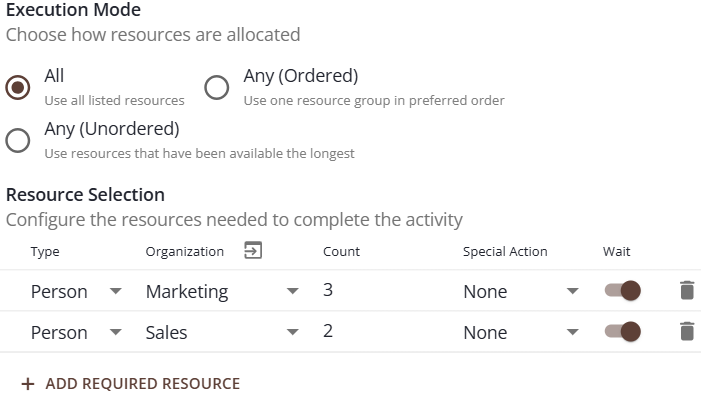
Specify the resources needed for a case to do the activity.
Execution Mode
All: Get all the resources in the list. This is an ‘AND;' All of the resources listed must be available (in schedule, and not acquired) to complete the task.
Any (Ordered): Try to get each group of resources (a group being, for example, 2 of type Any from Marketing), starting from the top, and stop if one of the groups is successfully acquired. If not, wait for any of the groups. This is an ‘OR,’ where the list is evaluated in order from top-to-bottom. In the example above, switching to Any (Ordered) would mean 3 Person type resources from Marketing OR 2 Person type resources from Sales could do this activity.
Any (Unordered): Get any of the listed resources, preferring whichever one has been available the longest. This is also an ‘OR,’ where the first available resource will be used; with a preference to acquire the least-utilized resource if more than one type is available at the same time. For example, if you have “Day Shift” and “Night Shift” that do not have overlapping schedules, the order doesn’t matter, and this option of ‘Any (Unordered)’ would get any available resource in schedule at the time the request is made.
Type
The type of the resource needed. The type can be “Any”, which means any resource from the organization will satisfy the request.
Organization
The organization the resource must come from. Current Swimlane means it will be the organization corresponding to the Lane (Swimlane) the shape is in. See Swimlane Based Resources for an explanation of how organizations can correspond to lanes.
Count
How many of the resource is needed. If Any (Unordered) is selected, there will be a total count rather than a count for each individual resource, and any resource acquired counts towards the total.
Special Action
By default, the resource is released when the task is complete. It is possible for the resource to still be needed to do subsequent activities, so if this field is set to “Acquire”, subsequent activities will require this resource, until it is released. To release, set the Special Action field to “Release”.
This is not possible when specifying Any (Ordered). If specifying Any (Unordered), the resource is released when “Release” is selected and the exact same list of resources is presented as specified when “Acquire” is selected.
Wait
This toggles whether the resource waits while other required resources are being acquired. If not, other activities that need the resource can take it during this time.
If specifying Any (Ordered), the simulation will try to acquire all the resources in the list, which will wait until the specified count of one group is acquired. It will then release all the other resources not part of that group. In the example above if Any (Ordered) is selected, it would acquire Person from Marketing and Person from Sales until it gets 3 from Marketing or 2 from Sales. If it acquired 2 from Sales, it would release the unused ones from Marketing.
Task
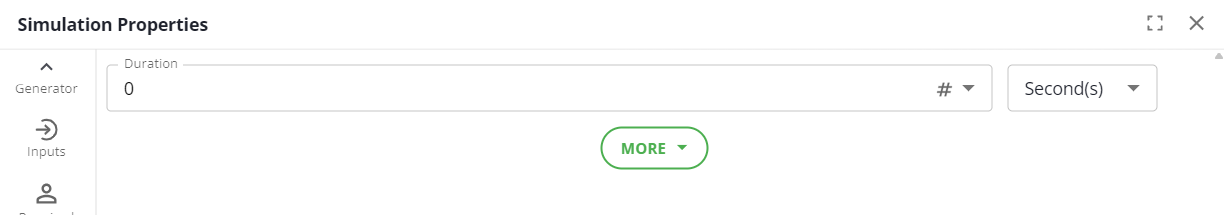
Duration
This is how long the activity takes to complete.
Outputs

Output
Specifies how to handle when an activity has multiple output paths.
First: Case goes down the first connector line it can find.
Duplicate: Case duplicates itself, sending one copy down each output path (if Split Type is set to “All Paths”) or specified paths (if Split Type is set to “Conditional”).
Split Into Family: Case splits itself into a case family, sending one member down each output path (if Split Type is set to “All Paths”) or specified paths (if Split Type is set to “Conditional”).
Decision: Case will go down one of the output paths, either based on probability (if Decision Type is set to “Percentage”) or based on the first condition to be satisfied (if Decision Type is set to “Conditional (First)”). If Conditional (First) is selected and all conditions are false, the case will go down the first output path.
Note that the “Percentage” is truly statistically random, and at low sample sizes (e.g., only 10 cases through a Decision) it is possible to get statistically significant deviations from the percentage you specify. For example, if you specify 50% Yes and 50% No, you might end up with 7 cases down the Yes path, and 3 down the No path.
Assignments
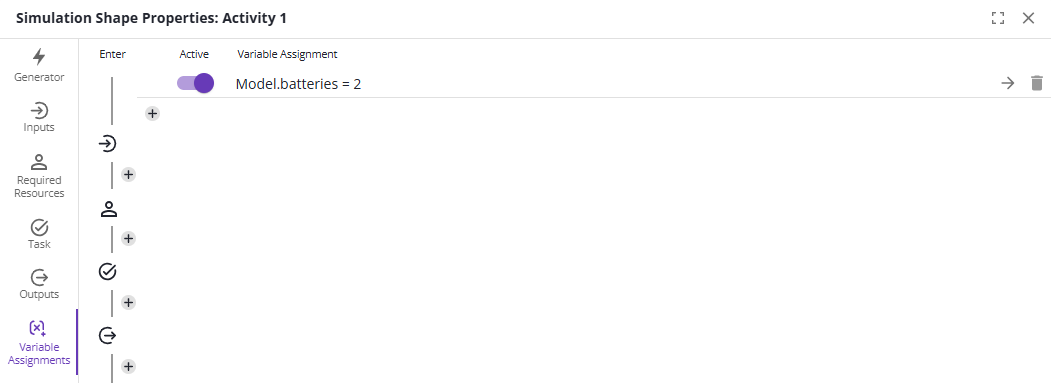
Change the values of variables.
Assignments can be placed at any of the 5 slots:
Enter: When the case arrives at the activity
After Input: After the case passes the Input gate if any
Before Task: After the case acquires required resources, right before the task starts
After Task: Right after the task finishes
Exit: When the case leaves the activity
Assignment Properties
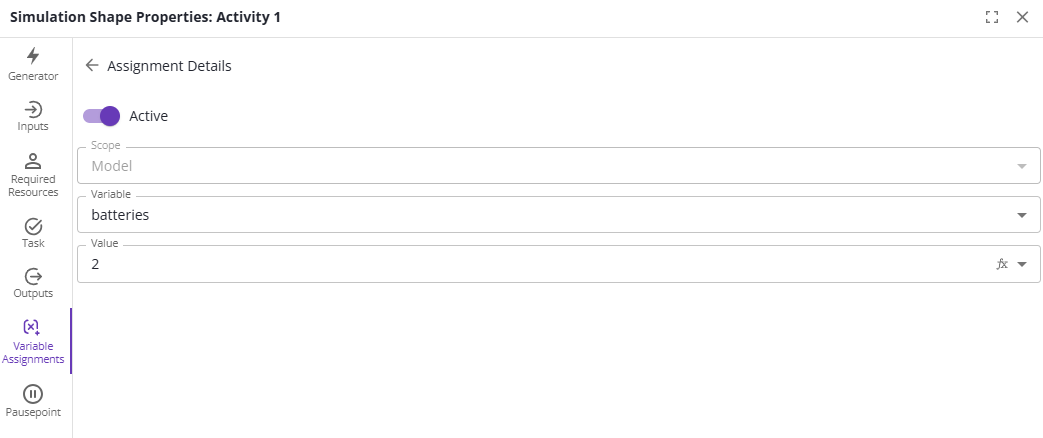
Active
Whether the assignment happens or not. If not, the assignment is ignored and the value of the variable is not changed.
Scope
If the same variable name exists in multiple scopes, select the scope; e.g., Scenario, Model, Case, etc.
Case Variable Scope (Base, Parent, Case)
Case variables may have 3 different scopes. If there is not a case family, then only the ‘case’ scope is available. If the case is part of a family, then either ‘parent’ or ‘base’ scope may apply, depending on where the case is in the family hierarchy. The scopes are:
Case: Change the value on this token only; no other tokens will be assigned at this time.
Parent: Change the value on the parent of this case, instead of the case directly. The parent is the case that this case was split from.
Base: Change the value on the ‘ancestor’ case that originated the family. If the token has been split, then one of its children was split, and one of the grandchildren assigned to ‘Base,’ it would be the ‘grandparent’ case value that is changed.
Variable
The variable to change the value of.
Value
The value to set the variable to.
Pausepoints
Pausepoints allow you to pause the simulation while running in trace mode. Pausepoints are potentially triggered whenever a case enters the activity that they are set up on. There are four types of pausepoints: Always, Expression True, Always After Count, Each Count.
Always: Triggers whenever a case enters the activity.
Expression True: Triggers if the given expression evaluates to true.
Always, After Count: Triggers after the given number of cases have entered. For example, if count is 3, then the first two cases will not trigger the pausepoint, but every case afterwards will.
Each Count: Triggers every nth case enters the activity. For example, if the count is 3, then the first two cases will not trigger the pausepoint, and the third case will trigger it. The fourth and fifth case will not trigger it, but the sixth will.
